
Outpatient Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is the surgical treatment for knee arthritis, where the damaged knee is removed and replaced with an artificial knee implant.

Robotic Knee Replacement
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Replacement is a treatment option for adults living with mid to late-stage osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.

Second Opinion on Joint Replacement & Complex Revisions
A second opinion on joint replacement or complex revisions is a second medical evaluation and treatment recommendation by a new doctor to verify the initial diagnosis and treatment plan suggested by your first doctor regarding undergoing joint replacement or revision of a failed joint replacement.

Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.

Unicompartmental/Partial Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant.

Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis.

Robotic Partial Knee Replacement
A partial knee replacement is a procedure to replace only the part of the knee joint that has arthritis with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and improve the function of the joint.

Correction of a Loose Knee Replacement
Reoperation of a total knee replacement to correct a loosened prosthesis as a result of wear and tear of the prosthetic joint surfaces is known as correction of a loose knee replacement.

Complex Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical treatment for painful arthritis of the knee in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.

Rapid Recovery Knee Replacement
Rapid recovery knee replacement, also known as an outpatient knee replacement, is an innovative procedure that is performed to replace a damaged knee joint with a prosthesis using minimally invasive techniques and surgical instruments that minimize post-operative pain and discomfort and promote faster recovery for patients.

Robotic Assisted Knee Replacement
Robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery is an alternative to the conventional knee replacement procedure.
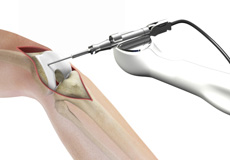
Robotic-Assisted Partial Knee Surgery
Robotic-assisted partial knee surgery is an innovative alternative to the conventional surgical procedure to treat degenerative knee diseases such as osteoarthritis.

After Knee Replacement
After knee replacement surgery, once the anesthesia wears off, you will start to experience pain, for which your doctor will prescribe medication.

Subchondroplasty
Subchondroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is performed to specifically repair chronic BMLs by filling them with a bone substitute material.

Partial Meniscectomy
Partial meniscectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the torn portion of the meniscus from the knee joint.

Partial Medial Knee Replacement
Partial medial knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the medial part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement.

Non-surgical Knee Treatments
The knee is a complex joint which consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that make joint movements easy and at the same time it is more susceptible to various kinds of injuries.

Intraarticular Knee Injection
Knee pain and stiffness can be disabling and difficult to treat. It can limit an individual’s lifestyle and negatively impact body image and emotional well-being.

Viscosupplementation aka Gel shots
Viscosupplementation refers to the injection of a hyaluronan preparation into the joint. These are often called “gel shots”, because they appear as a clear gel.

Physical Therapy for Knee
Physical therapy is an exercise program that helps you to improve movement, relieve pain, encourage blood flow for faster healing, and restore your physical function and fitness level.

Chondromalacia Patella
Chondromalacia patella is a common condition characterized by softening, weakening and damage of the cartilage.

Kneecap Bursitis
Bursitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of the bursa. Inflammation of the bursa in front of the kneecap (patella) is known as kneecap bursitis or prepatellar bursitis.

Knee Injury
Pain, swelling, and stiffness are the common symptoms of any damage or injury to the knee. If care is not taken during the initial phases of injury, it may lead to joint damage, which may end up destroying your knee.

Meniscal Injuries
Meniscal tears are one of the most common injuries to the knee joint. It can occur at any age but are more common in athletes involved in contact sports.

Meniscal Tears
A meniscal tear is a common knee injury in athletes, especially those involved in contact sports. A sudden bend or twist in your knee causes the meniscus to tear.

Knee Arthritis
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. Arthritis is a general term covering numerous conditions where the joint surface or cartilage wears out.

Periprosthetic Knee Fractures
Knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial implants.

Knee Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people.

Anterior Knee Pain
Anterior knee pain is characterized by chronic pain over the front and center of the knee joint. It is common in athletes, active adolescents (especially girls) and overweight individuals.
Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee’s normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Having a well-functioning healthy knee is essential for our mobility and ability to participate in various activities. Understanding the anatomy of the knee enhances your ability to discuss and choose the right treatment procedure for knee problems with your doctor.
Bones of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). There are two round knobs at the end of the femur called femoral condyles that articulate with the flat surface of the tibia called the tibial plateau. The tibial plateau on the inside of the leg is called the medial tibial plateau and on the outside of the leg, the lateral tibial plateau.
The two femoral condyles form a groove on the front (anterior) side of the knee called the patellofemoral groove. A small bone called the patella sits in this groove and forms the kneecap. It acts as a shield and protects the knee joint from direct trauma.
A fourth bone called the fibula is the other bone of the lower leg. This forms a small joint with the tibia. This joint has very little movement and is not considered a part of the main joint of the knee.
Articular Cartilage and Menisci of the Knee
Movement of the bones causes friction between the articulating surfaces. To reduce this friction, all articulating surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage. The articulating surface of the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus and the back of the patella are covered with this cartilage. The cartilage provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction between the articulating surfaces of the bones, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones inside the joint capsule.
Within the knee joint, between the femur and tibia, are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci. Menisci function to provide stability to the knee by spreading the weight of the upper body across the whole surface of the tibial plateau. The menisci help in load-bearing i.e. it prevents the weight from concentrating onto a small area, which could damage the articular cartilage. The menisci also act as a cushion between the femur and tibia by absorbing the shock produced by activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint. There are two important groups of ligaments that hold the bones of the knee joint together, collateral and cruciate ligaments.
Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee. They prevent the knee from moving too far during side-to-side motion. The collateral ligament on the inside is called the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the collateral ligament on the outside is called the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Cruciate ligaments, present inside the knee joint, control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee - the quadriceps and the hamstrings, which enable movement of the knee joint. The quadriceps muscles are located in front of the thigh. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the knee straightens. The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh. When the hamstring muscles contract, the knee bends.
Tendons of the Knee
A tendon is a tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The quadriceps muscles of the knee meet just above the patella and attach to it through a tendon called the quadriceps tendon. The patella further attaches to the tibia through a tendon called the patella tendon. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon all work together to straighten the knee. Similarly, the hamstring muscles at the back of the leg are attached to the knee joint with the hamstring tendon.




